What is Laparoscopic Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection (LPLND)?
Laparoscopic Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection (LPLND) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure primarily utilised in the treatment of cancers affecting organs near the pelvic region. This technique involves using small abdominal incisions to insert specialised instruments and a scope camera to visualise and manipulate pelvic structures to achieve precise lymph node removal for cancer treatment.
During an LPLND surgery, lymph nodes and the adherent fat tissue in the pelvic region are carefully removed. These lymph nodes play a crucial role in filtering lymphatic fluid and are often a site where cancer cells may spread, necessitating their removal for therapeutic purposes. By dissecting and excising these lymph nodes, surgeons aim to prevent the further spread of cancer and improve patient outcomes.
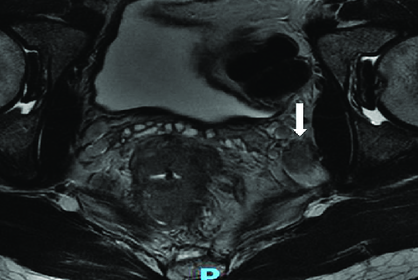
Challenges Faced in LPLND Surgeries
Our industry mentors, Professor Fernando Bello from Duke-NUS Medical School and Dr Khor Shao Nan from the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Singapore General Hospital, have shared a few areas that underscore the challenges in LPLND. These key issues include:
Complexity of Pelvic Anatomy
The intricate nature of pelvic anatomy complicates surgical procedures, requiring surgeons to navigate through densely packed structures with precision and accuracy.
Inability to Visualise Spatial Relationships
Surgeons encounter difficulties in visualising spatial relationships within the pelvic region, hindering their ability to perform precise surgical manoeuvres effectively.
Rarity of LPLND Cases
The scarcity of LPLND cases, approximately 10-15 annually in Singapore, limits opportunities for surgeons to gain practical experience and proficiency in the procedure.
Understanding the Needs of Surgeons
Our primary target audience comprises surgeons preparing for the LPLND procedure and each user group faces distinct challenges:

General Surgery Resident (GSR)
Difficulty in orienting to laparoscopic view

Colorectal Surgery Fellow (CSF)
Limited resources to prepare for LPLND cases due to rarity of procedure

Senior Consultant (SC)
Lack of avenue to assess proficiency in LPLND
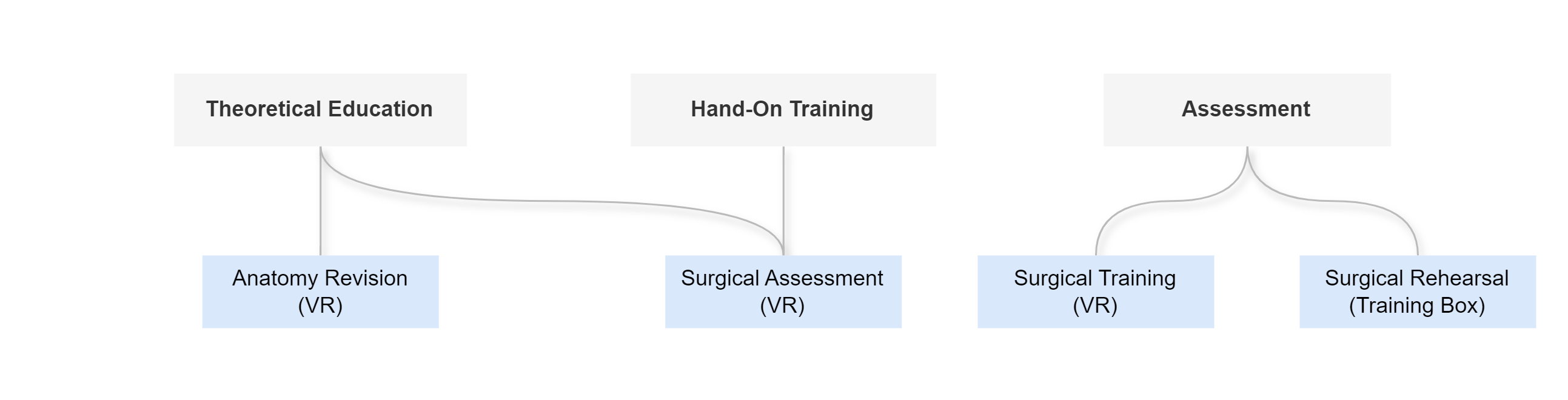
How might we develop an immersive simulation device for surgeons to support the learning and practice of LPLND and increase their confidence levels in performing the surgery?
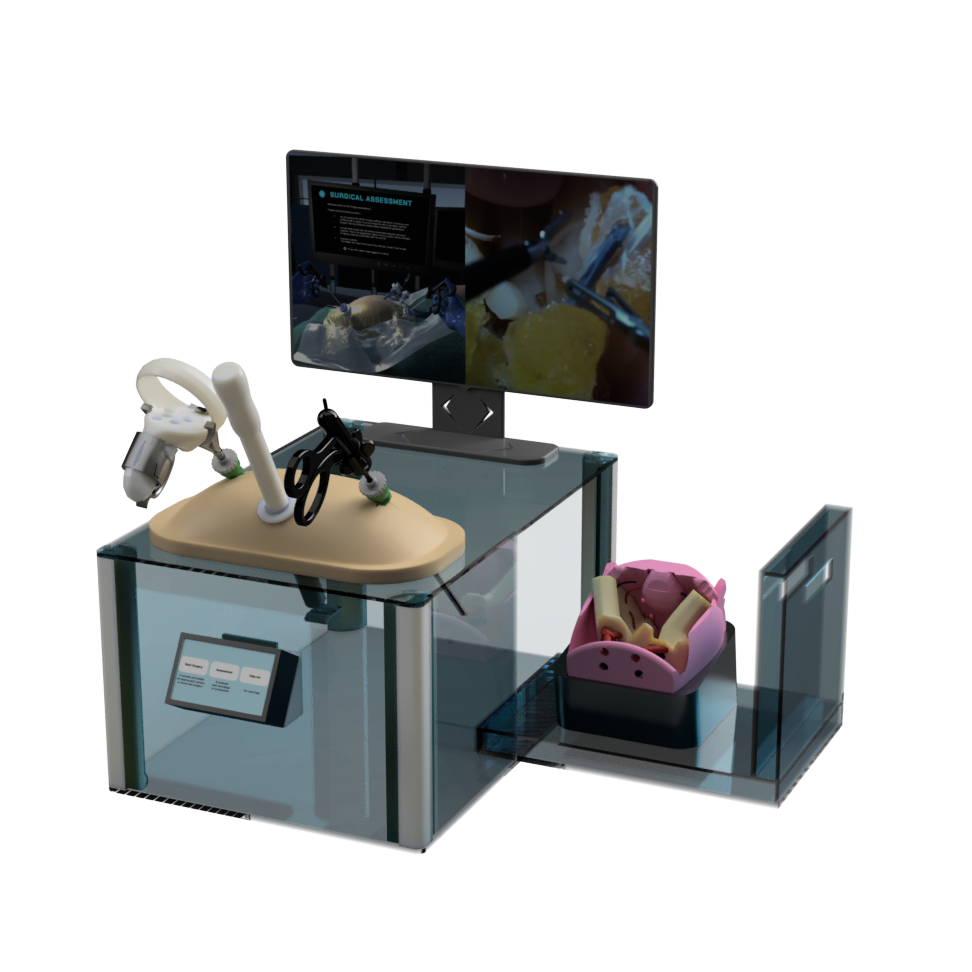
Introducing LaparoLymph
A combination of VR simulation and a physical training box to provide a comprehensive learning experience on LPLND surgery.
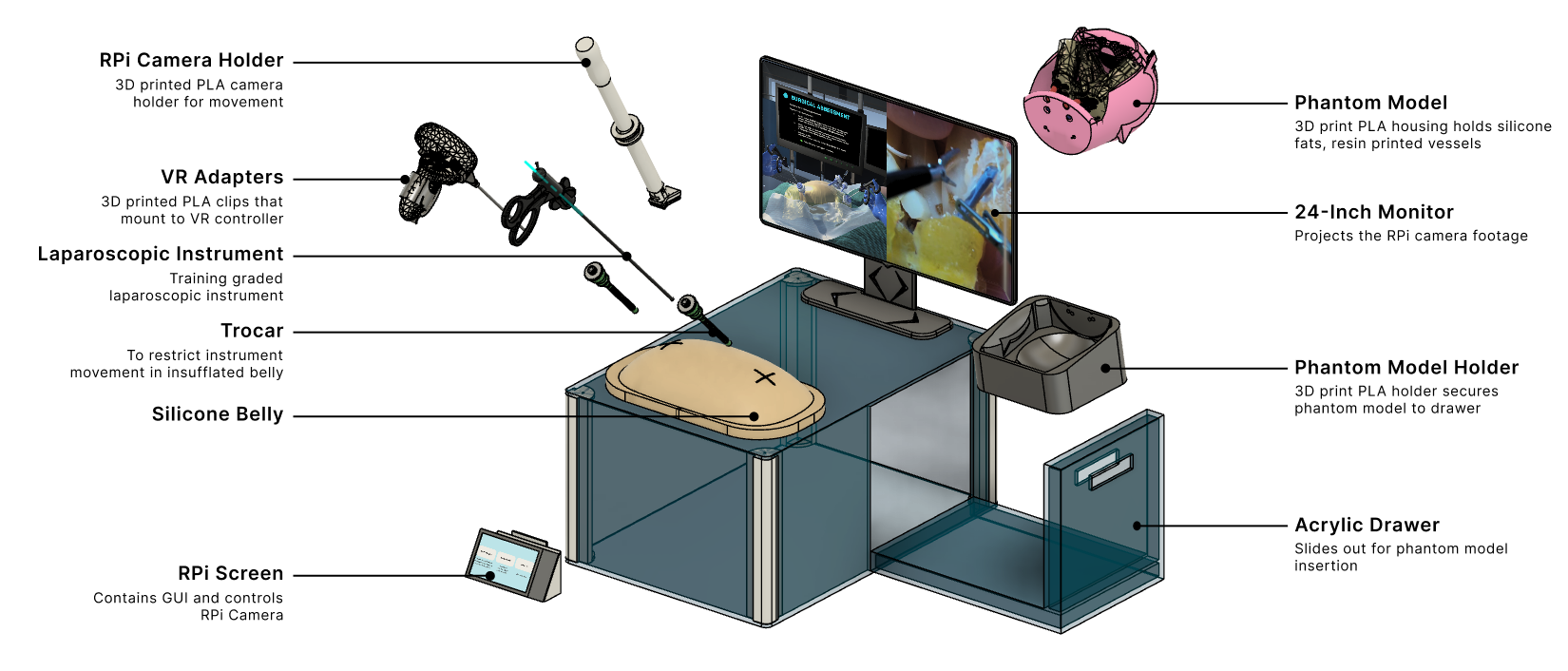
LaparoLymph provides 4 main features, each designed to fulfil the following 3 objectives, each tailored to address the unique needs of our users

General Surgery Residents (GSR)
Provides GSRs a review of pelvic anatomy and its visualisation through laparoscope

General Surgery Residents (GSR)

Senior Consultants (SC)
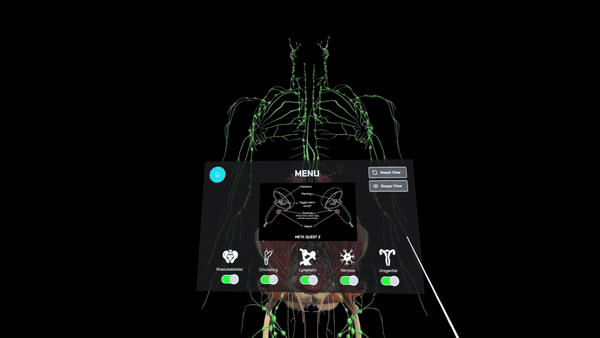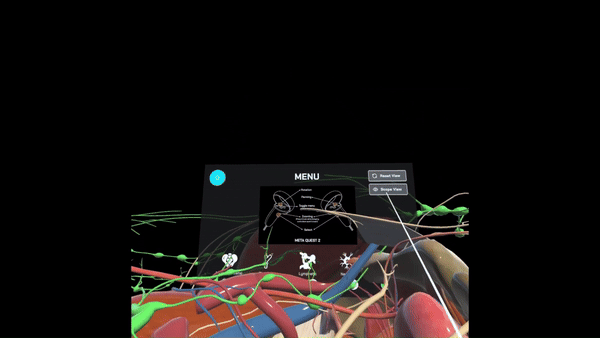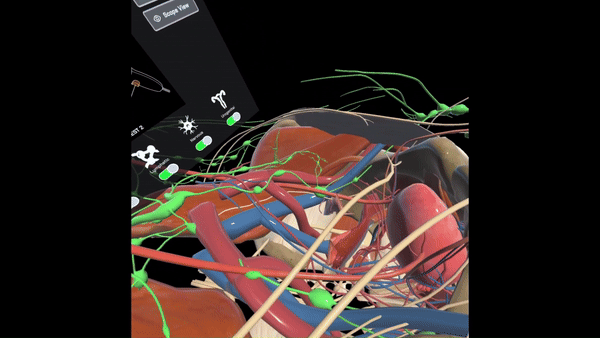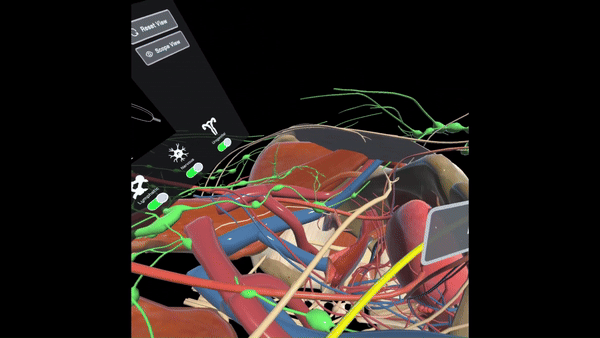
Anatomy Revision
Provides surgeons with a comprehensive understanding of pelvic anatomy through 3D spatial exploration, allowing them to toggle between different organ systems and manipulate views to enhance learning and familiarity with anatomical structures in the pelvic region.



General Surgery Residents (GSR)
Provides step-by-step guidance for GSRs with learning LPLND.

General Surgery Residents (GSR)
Provides reinforced practical training for CSFs with limited exposure to LPLND cases

Senior Consultants (SC)
Surgical Training
Provides theoretical education on the steps involved in LPLND surgery through a guided surgical training with detailed instructions of each step.
7 Sections, 3 Step Types
The entire LPLND surgery is broken down into 7 key sections, each containing multiple steps. Surgeons can repeatedly practice the steps, enhancing their skill acquisition and retention.
Among the 7 sections, surgeons are tasked to complete 3 types of steps:
- Identification of crucial landmarks
- Dissection of tissues/lymph node bundles
- Extraction of dissected lymph node bundles




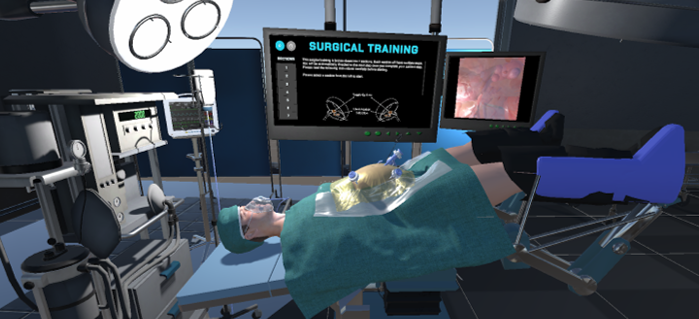
Realistic Operating Theatre
Patient positioned at Lloyd-Davies position with Trendelenburg tilt

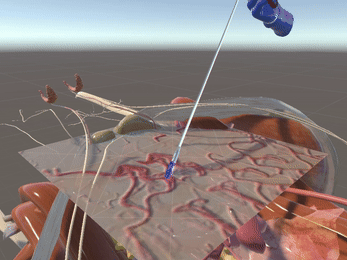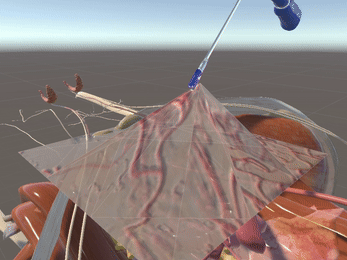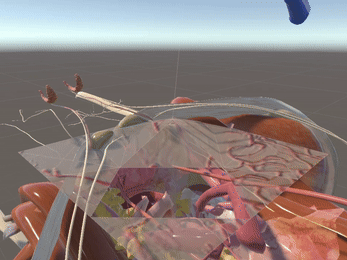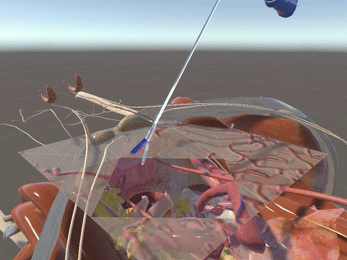
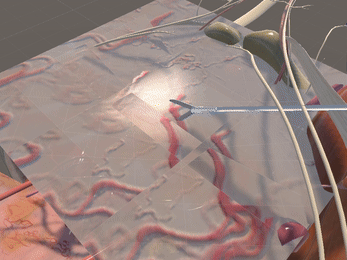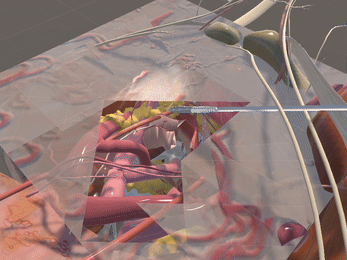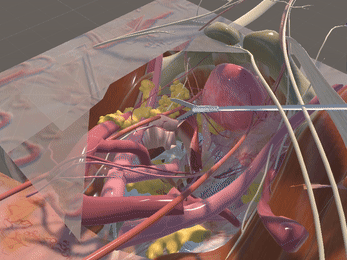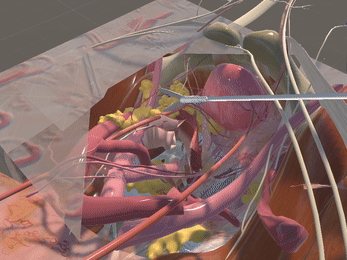

Simulation of Physics & Tool Interactions
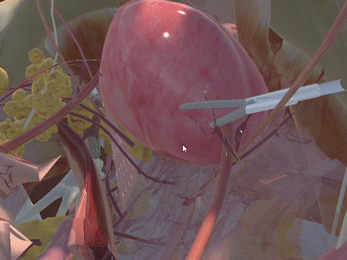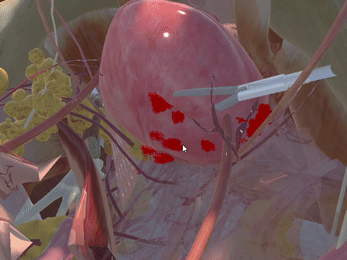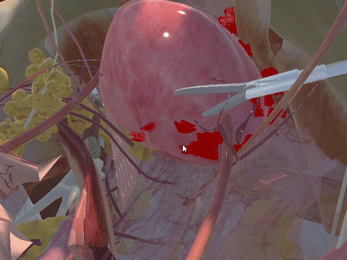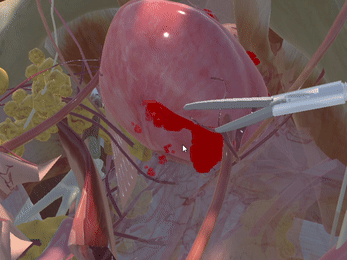

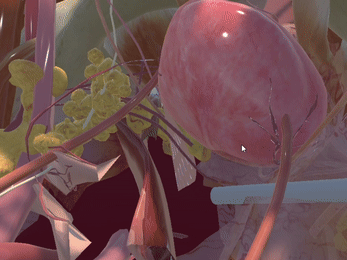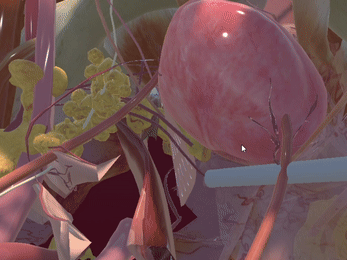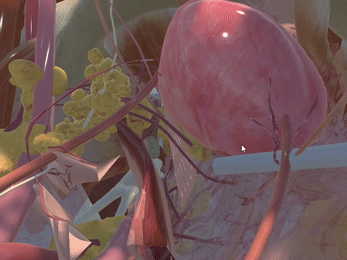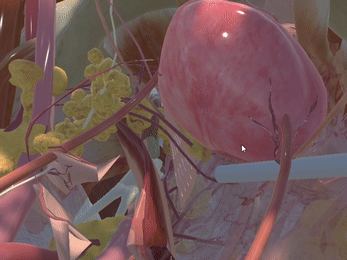
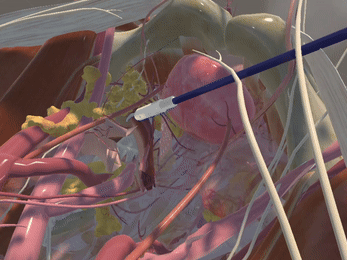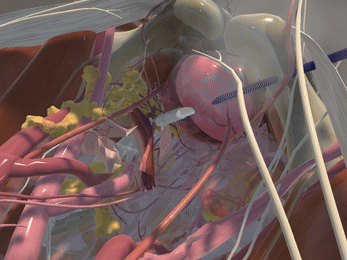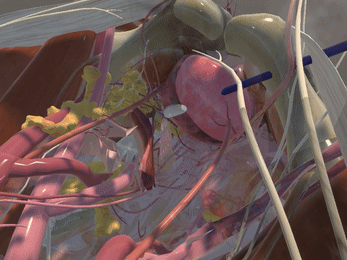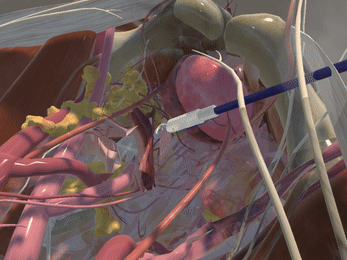
Immersive Environment
Simulated restriction of laparoscopic tool movement facilitated by:
Physical Box Trainer with Trocars
Controller Adaptors
Rotary Encoders for Tool Rotation
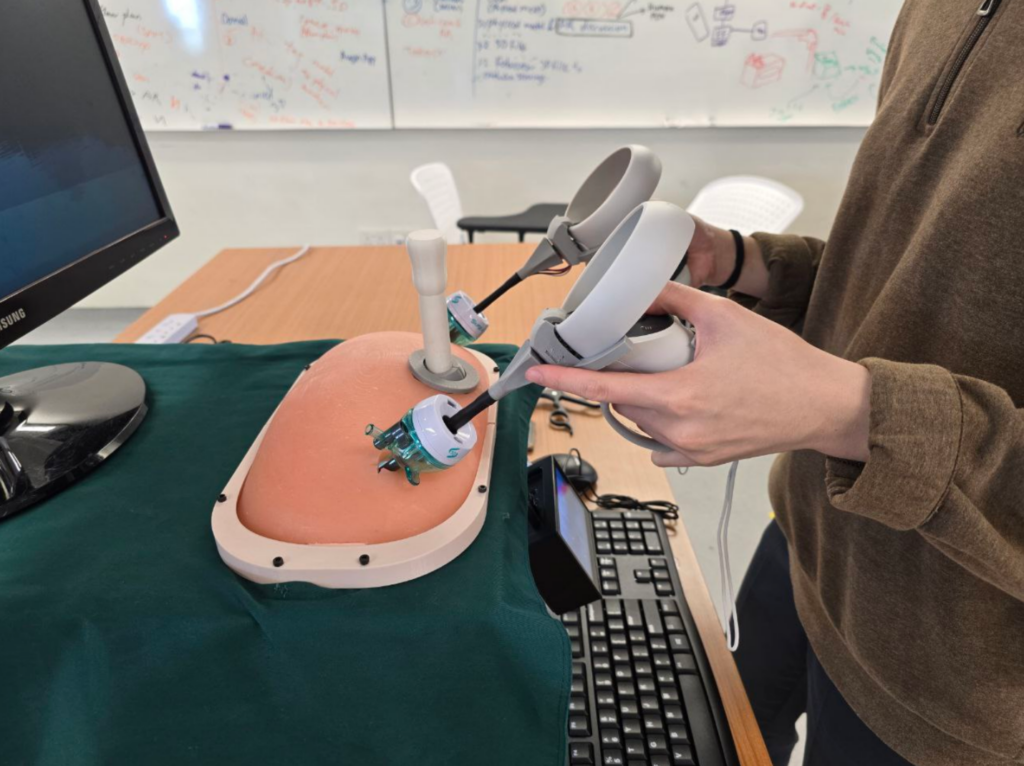

Physical Box Trainer with Trocars
Controller Adapters

Rotary Encoders for Tool Rotation

General Surgery Residents (GSR)

General Surgery Residents (GSR)

Senior Consultants (SC)
Provide a means for SCs to measure and evaluate their proficiency in LPLND.
Surgical Assessment
In this stage, we implement an assessment function aimed at evaluating surgeons’ proficiency in LPLND,
providing feedback on accuracy, time taken, and successful removal of the lymphatic fat tissues.
Replicates real-life surgical scenarios,
emphasizing the irreversible nature of mistakes


Provides feedback on user performance

General Surgery Residents (GSR)

General Surgery Residents (GSR)

Senior Consultants (SC)
Provide a means for SCs to measure and evaluate their proficiency in LPLND.
Surgical Rehearsal
In this stage, users interact with a pelvic phantom, offering a realistic haptic feedback experience. Integrated with the Physical Box Trainer, this stage assesses users’ technical skills using the Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS) and Fat Clearance Assessment, enhancing proficiency through simulated practice and feedback.
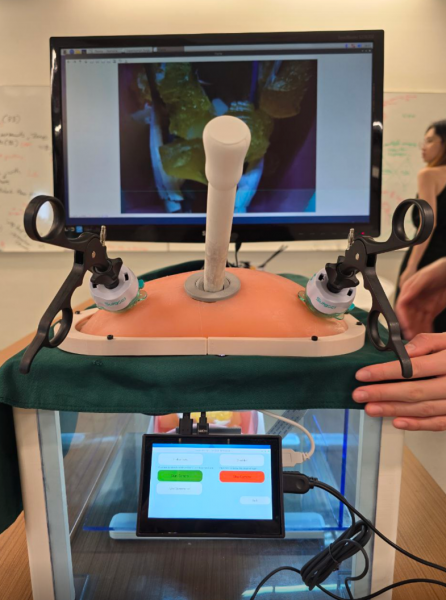
Pelvic Phantom
Materials chosen matches the tactility of real anatomical components
Replaceable design allows for customization with appropriate dissections
Segmentation of pelvic anatomy optimises reusability by including only selected components
Single-use packages prioritize areas with higher user interaction, such as lymphatic fat tissue and central vasculature.
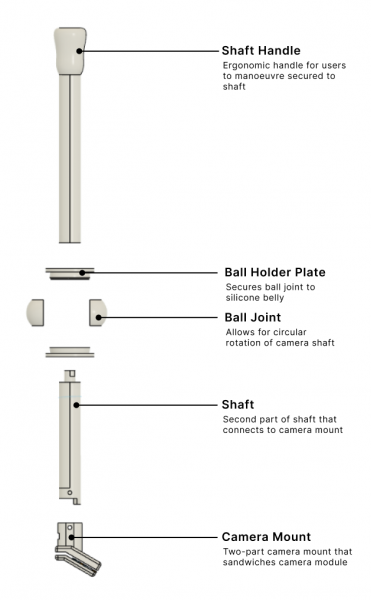
Camera and Holder
The electronic components chosen for the surgical camera were carefully selected to meet both spatial and technical specifications.
Combined with custom camera holder for translational and rotational capabilities.
Integration into RaspberryPi GUI provides low-latency, high-quality visual feed similar to actual operations.



Respect for Tissue
Involves a Computer Vision model that distinguishes between allowable and risky surgical actions, penalising users for any identified risky motions
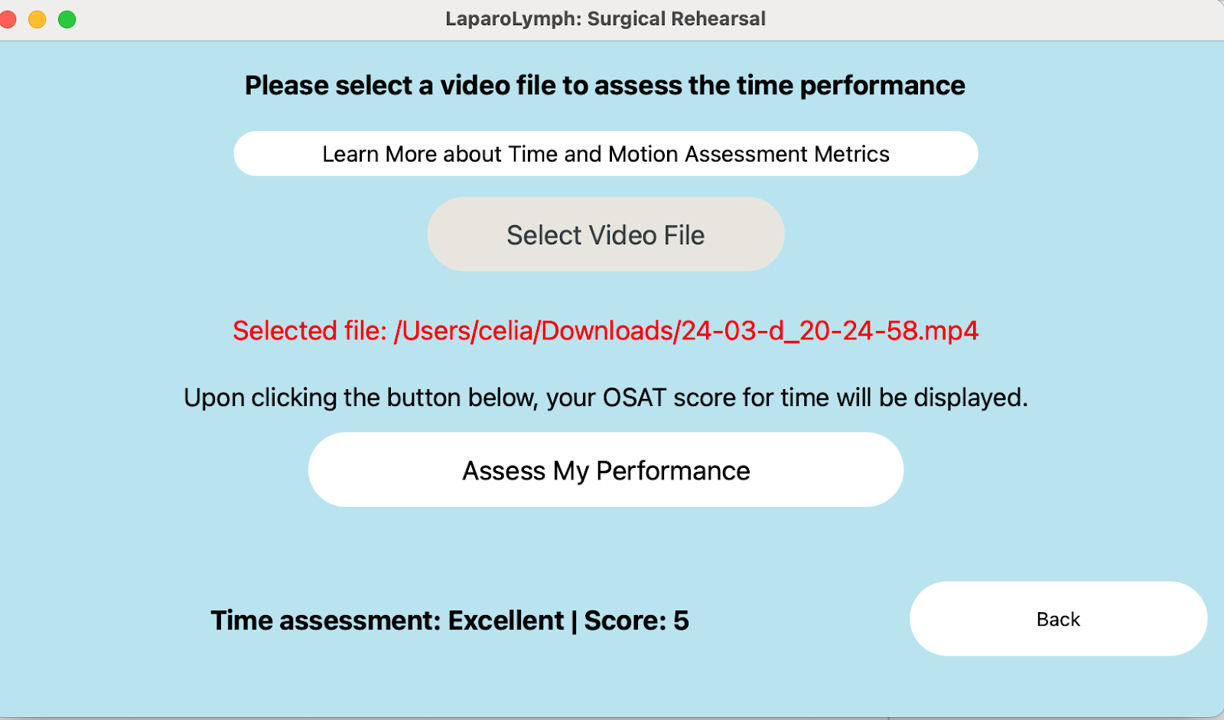
Time and Motion
Assesses the length of recorded mock surgeries against an ideal threshold, emphasising the importance of speed in LPLND procedures
Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS)
The OSATS metrics are displayed on the RaspberryPi (RPi) touchscreen, providing users with objective feedback on their performance.
Within the OSATS framework, there are two key components can be assessed:
- Respect for Tissue
- Time and Motion
Fat Clearance Assessment
Employs a CV colour detection model to quantify the degree of fat removal in the pelvic phantom, providing valuable feedback on the user’s performance.

Acknowledgements
Capstone Instructor — Dr. Edwin Koh
For guiding, supporting, and mentoring throughout the development of this project
Writing Instructor — Dr. Delfinn Tan
For providing valuable insights and assistance in refining the written components of our project.
Industry Partner — Duke NUS
For providing us with the opportunity to undertake this project and for their continuous support
Industry Mentor — Prof. Fernando Bello
For providing guidance, support, and mentorship throughout the development of this project
Industry Mentor — Dr. Khor Shao Nan
For providing valuable input and feedback as a practising surgeon, enriching our understanding of LPLND.












